Hormone Imbalance
Hormones are your body’s chemical messengers. Produced in the endocrine glands, these powerful chemicals travel around your bloodstream telling tissues and organs what to do. They help control many of your body’s major processes, including metabolism and reproduction.When you have a hormonal imbalance, you have too much or too little of a certain hormone. Even tiny changes can have serious effects throughout your whole body.
Your hormones play an integral role in your overall health. Because of that, there’s a broad range of symptoms that could signal a hormonal imbalance. Your symptoms will depend on which hormones or glands aren’t working properly.
Some examples are:
- weight gain, rounded or puffy face,
- fatigue
- nervousness, anxiety
- muscle aches, pain, joint swelling
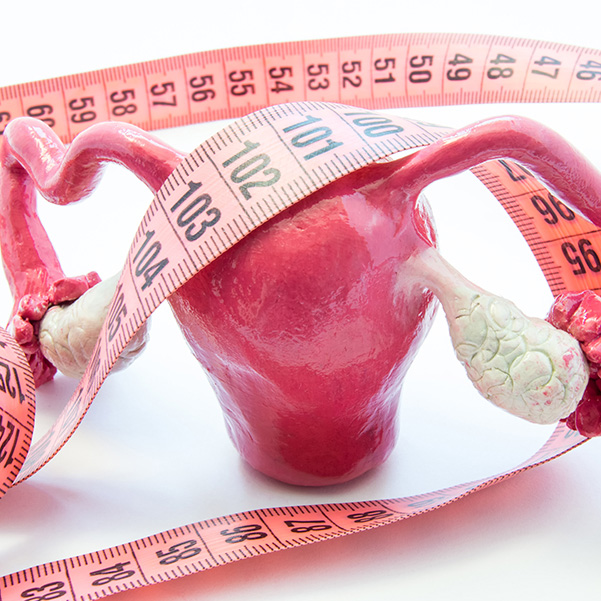
What are Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are tumors that grow in a woman's uterus. These growths are typically not cancerous (benign).The exact cause of fibroids is not known. In women who have symptoms, the most common symptoms of uterine fibroids include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Prolonged menstrual periods - seven days or more of menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pressure or pain
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty emptying your bladder
- Constipation
- Backache or leg pains



